California is one of the most wildfire-prone states in the United States. Each year, millions of acres are affected by fires that are often intensified by specific weather conditions. Understanding California wildfire weather conditions is essential for residents, property owners, and travelers who want to stay informed and prepared.
This comprehensive guide explains the weather patterns that fuel wildfires in California, how forecasts predict fire risk, and what safety measures should be taken during high-risk periods.
Why California Is Highly Vulnerable to Wildfires
California’s wildfire risk is influenced by a combination of:
- Prolonged dry seasons
- Hot temperatures
- Strong seasonal winds
- Mountainous terrain
- Dense vegetation
The state’s Mediterranean climate features wet winters and long, dry summers. During summer and fall, vegetation becomes extremely dry, creating ideal fuel for fires.
Key Weather Conditions That Increase Wildfire Risk
Several weather factors significantly increase wildfire danger in California.
1. High Temperatures
Hot weather dries out grass, shrubs, and forests. When temperatures rise above normal for extended periods, moisture evaporates quickly from vegetation, making it highly flammable.
Heatwaves can accelerate fire spread once a fire starts.
2. Low Humidity
Humidity measures the amount of moisture in the air. Low humidity levels—often below 20 percent—create extremely dry conditions.
Dry air allows fires to ignite easily and spread rapidly.
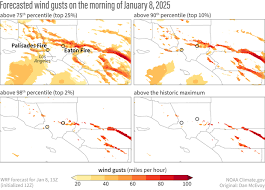
3. Strong Winds
Wind is one of the most dangerous wildfire factors. Strong winds can:
- Carry embers over long distances
- Spread flames rapidly
- Change fire direction suddenly
In California, certain seasonal wind events significantly increase fire risk.
Santa Ana and Diablo Winds
Two major wind systems contribute to wildfire conditions:
Santa Ana Winds (Southern California)
- Typically occur in fall and winter
- Bring hot, dry air from inland deserts
- Can reach high speeds
- Dramatically lower humidity
These winds are often associated with major wildfire outbreaks.
Diablo Winds (Northern California)
- Occur mainly in fall
- Bring dry, gusty conditions
- Increase fire spread potential
When combined with dry vegetation, these winds create extremely dangerous fire weather conditions.
Drought and Dry Vegetation
California frequently experiences drought cycles. During drought:
- Soil moisture levels drop
- Trees and plants become stressed
- Dead vegetation accumulates
Dry fuel increases the likelihood of ignition and rapid fire growth.
Long-term drought conditions have been linked to larger and more intense wildfires.
Lightning Storms
Although less common than wind-driven fires, lightning can ignite wildfires, especially during dry thunderstorms.
Dry lightning storms produce minimal rainfall but generate lightning strikes capable of starting multiple fires at once.
These events have caused significant wildfire outbreaks in Northern California.
Fire Weather Warnings and Red Flag Alerts
The National Weather Service issues specific alerts during high-risk conditions.
Red Flag Warning
A Red Flag Warning indicates:
- Strong winds
- Low humidity
- Warm temperatures
- Critical fire weather conditions
During a Red Flag Warning, outdoor burning and certain activities may be restricted.
Fire Weather Watch
This alert is issued when critical conditions are possible in the near future.
Residents should monitor forecasts closely during these alerts.
Seasonal Wildfire Patterns in California
Summer (June to August)
- Hot temperatures
- Very dry vegetation
- Increased wildfire activity
Fall (September to November)
- Peak wildfire season in many areas
- Santa Ana and Diablo winds
- Extremely low humidity
Winter (December to February)
- Rain reduces fire risk
- However, dry winters can extend wildfire season
Spring (March to May)
- Moderate risk depending on rainfall patterns
In recent years, wildfire season has extended beyond traditional timeframes due to changing climate patterns.
Climate Change and Wildfire Intensity
Research indicates that climate change is contributing to:
- Higher average temperatures
- Longer dry seasons
- Increased frequency of heatwaves
- Reduced snowpack in mountain regions
These changes result in longer wildfire seasons and more intense fires.
Warmer conditions also increase the likelihood of rapid fire spread.
Impact of Wildfire Weather on Air Quality
Wildfires significantly affect air quality across California.
Smoke can:
- Travel hundreds of miles
- Increase particulate matter in the air
- Trigger respiratory issues
Air Quality Index (AQI) levels may rise to unhealthy or hazardous categories during active fire events.
Sensitive individuals, including children and older adults, are particularly vulnerable.
How Fire Behavior Is Forecasted
Meteorologists use several tools to forecast wildfire conditions:
- Weather models
- Satellite imagery
- Wind speed predictions
- Fuel moisture measurements
- Temperature and humidity trends
These forecasts help emergency services prepare resources and issue public warnings.
How to Prepare During High Fire Weather
When wildfire weather conditions are elevated:
1. Create a Defensible Space
Clear dry vegetation around homes to reduce fire risk.
2. Prepare an Emergency Kit
Include:
- Water and non-perishable food
- Flashlights and batteries
- Important documents
- Face masks for smoke protection
3. Have an Evacuation Plan
Know evacuation routes and keep vehicles fueled.
4. Monitor Official Alerts
Follow updates from:
- National Weather Service
- CAL FIRE
- Local emergency management agencies
Travel Considerations During Wildfire Season
Travelers should:
- Check fire maps before visiting affected regions
- Monitor road closures
- Be aware of air quality advisories
- Have flexible travel plans
Wildfires can impact highways, parks, and outdoor recreation areas.
Frequently Asked Questions
What weather causes wildfires in California?
High temperatures, low humidity, strong winds, and dry vegetation create ideal wildfire conditions.
When is wildfire season in California?
Peak season typically occurs in summer and fall, though fires can happen year-round.
What is a Red Flag Warning?
It is an alert indicating critical fire weather conditions that increase wildfire risk.
Do wildfires only happen in forests?
No. Grasslands, shrublands, and urban-wildland areas are also vulnerable.
Is wildfire season getting longer?
Recent trends suggest that wildfire season has expanded due to warmer and drier conditions.
Final Thoughts
California wildfire weather conditions are driven by a complex combination of heat, drought, wind, and low humidity. Seasonal wind events such as Santa Ana and Diablo winds play a major role in increasing fire danger, especially during fall.
As climate patterns evolve, wildfire seasons have become longer and more intense. Staying informed about Red Flag Warnings, monitoring forecasts, and preparing emergency plans are essential steps for protecting lives and property.
Understanding how weather influences wildfire behavior helps residents and visitors make safer decisions during high-risk periods.
Leave a Reply